Summary
This article delves into the intricate relationship between language, truth, and logic in football, revealing how historical context and technology shape our understanding of the game. Key Points:
- Explore how technological advancements, such as VAR and high-definition replays, have transformed football tactics and our understanding of fairness.
- Analyze the evolution of iconic formations like the 'W-M' and their modern reinterpretations, highlighting the interplay between historical tactics and current practices.
- Investigate the shift from centralized to decentralized defensive strategies in football, focusing on how tactics like M-Defense have adapted to contemporary gameplay.

Three years ago, I penned this essay, and I've decided to share an updated version today. By the end of your reading, you’ll likely grasp the reason behind the title of this blog.
Key Points Summary
- The 4-3-3 formation emphasizes attacking play and width, making it effective for teams that want to dominate possession.
- The 4-2-3-1 formation provides a strong midfield presence, allowing for both defensive stability and attacking creativity.
- The classic 4-4-2 is known for its simplicity and balance but can struggle against more fluid formations in modern football.
- The 4-4-2 diamond offers a compact midfield structure, enhancing control but potentially leaving the flanks exposed.
- A 3-5-2 formation focuses on solid defense with wing-backs contributing to attack, though it requires disciplined players to maintain shape.
- Tactics like `Pass and Move` highlight the importance of quick decision-making in maintaining possession during matches.
Football tactics are essential for creating a successful game plan. Different formations cater to various styles of play, whether it`s an aggressive attack or sturdy defense. Understanding these tactics not only makes watching games more enjoyable but also deepens our appreciation of how teams strategize on the pitch. Everyone loves a good match where every pass and movement counts!
Extended Comparison:| Formation | Strengths | Weaknesses | Current Trends | Expert Opinions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4-3-3 | Emphasizes attacking play and width, effective for possession dominance. | Can be vulnerable defensively if wingers do not track back. | Increased use of false nines to create space and confuse defenders. | Recommended by coaches like Pep Guardiola for its flexibility. |
| 4-2-3-1 | Strong midfield presence, allows for defensive stability and attacking creativity. | Can be overrun in midfield against teams with more dynamic formations. | Popular among teams looking to balance attack and defense, especially in counter-attacking play. | Favored by managers like José Mourinho for its versatility. |
| 4-4-2 | Known for simplicity and balance, good overall structure. | Struggles against fluid formations; can become predictable. | Revival in lower leagues but less common at the top level due to tactical evolution. | Considered outdated by some analysts but praised for youth development. |
| 4-4-2 Diamond | Compact midfield enhances control and ball retention. | Leaves flanks exposed; requires highly disciplined players. | Adopted by teams focusing on possession-based football while exploiting central spaces. | Used effectively by teams like Leicester City during their title-winning season. |
| 3-5-2 | Solid defense with wing-backs contributing offensively; adaptable to various game situations. | Requires high fitness levels and discipline from players to maintain formation. | Gaining traction as a counter-strategy against dominant possession-based tactics. | Seen as a tactical evolution that provides flexibility, endorsed by modern managers. |
Understanding Football History: Context and Technology′s Impact
"**1. The Importance of Contextual Understanding:** The passage emphasizes the necessity of contextualizing historical analysis in sports, particularly regarding language evolution and tactical changes that can affect our perception of the game's history. This approach is crucial for evaluating past players as it allows a consideration of how formations, playing styles, and game tempo have evolved over time. By doing so, we can avoid anachronistic comparisons and gain a deeper understanding of the historical significance of players like Trent Alexander-Arnold, whose role is shaped by the complexities of modern football.","**2. The Role of Technology and Media in Shaping Perception:** The example illustrates how technology and media influence our understanding of football. Today's fans experience the sport through high-definition visuals, slow-motion replays, and detailed statistics. While this accessibility enhances enjoyment, it may also skew perceptions of history. Sports industry professionals should remain aware that earlier eras lacked advanced technology, leading to different emphases on aspects such as individual player statistics. Acknowledging this dynamic is vital for accurately interpreting historical information and appreciating the sport's evolution."
Beyond Bad Habits: Evolving Tactics in Modern Football
In modern football, it's essential to approach "bad habits" not as detrimental practices but as opportunities for tactical evolution. The game has transcended traditional methods; instead of simply eliminating outdated tactics, teams are focused on innovating and adapting their strategies. This is evident in trends such as gegenpressing and the utilization of false nines, which represent significant advancements rather than mere deviations from the norm. High-level teams continuously challenge conventional thinking by embracing these innovations rather than reverting to previous styles.Moreover, the increasing reliance on data and analytics poses both an opportunity and a challenge within football. While quantitative analysis offers valuable insights, it can sometimes obscure fundamental principles of the game. To truly enhance decision-making processes in football, it's crucial to find a balance between data-driven approaches and qualitative understanding rooted in experience. Effective thinking in this sport necessitates an integration of statistical language with intuitive knowledge gained through years of engagement with football.
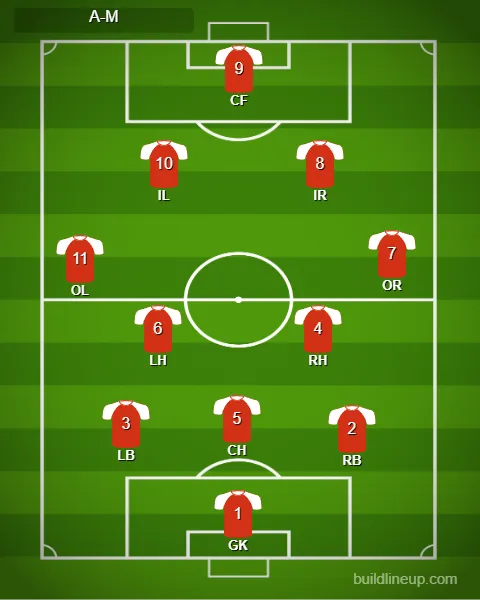
Classic Football Positions and Their Designations:
Goalkeeper
Right Full-Back
Left Full-Back
Right Half-Back
Center Half-Back
Left Half-Back
Outside Right
Inside Right
Center Forward
Inside Left
Outside Left
Tactical Formations: W-W / 4–3–3

The image featured at the top of this page illustrates a visual guide to the classic pyramid formation, known as the 2–3–5 setup. This formation emerged during football's formative years and remained prevalent for many decades. The term "full-back" was coined to identify the players positioned deepest on the field—those who operated "fully back" from the attacking front line. Meanwhile, a half-back occupied a space roughly halfway back on the pitch, akin to what we now refer to as an attacking defender or defensive midfielder.
The 2–3–5 formation may seem extremely aggressive by contemporary standards, yet when we examine one of the most prevalent formations in today’s football—namely the point-down 4–3–3 with two wingers—we find it bears a striking resemblance to its classical predecessor. The distinction between these formations largely comes down to terminology; the former can be seen as an offensive interpretation of the latter. Historical accounts of football's gameplay prior to the offside law changes in 1925 suggest that what we now recognize as a 4–3–3 was essentially a more defensive adaptation of the original pyramid shape.
The W-M/3–2–5 formation is a strategic approach in football that emphasizes both offensive and defensive capabilities. By utilizing three forwards, two midfielders, and five defenders, it creates a solid defensive line while maintaining the ability to launch swift counterattacks. This structure allows teams to adapt quickly depending on the match situation, making it versatile for various opponents. Coaches often prefer this setup for its balance between protecting the goal and seizing scoring opportunities.}
{In implementing the W-M/3–2–5 formation, coaches must ensure that players are well-coordinated and understand their specific roles on the field. Each player’s positioning is crucial; forwards should focus on pressing high up to regain possession quickly, while midfielders link play between defense and attack. Defenders need to communicate effectively to maintain their shape and cover spaces efficiently. Training sessions typically emphasize these dynamics to enhance team cohesion during matches.}
{Historically, this formation gained prominence in early 20th-century football as teams began recognizing the importance of structured gameplay over chaotic styles. Its origins trace back to when clubs aimed at maximizing their tactical approach against opponents with varying strengths. The evolution of the game has led many modern teams to reintroduce elements of this classic setup, blending traditional strategies with contemporary tactics for optimal performance on the pitch.

Responses to this shift varied significantly among teams. In regions like Southern Europe and Latin America, the predominant tactic was the W-W formation mentioned earlier. As the playing area expanded, inside forwards began to retreat further back to ensure a seamless connection between midfield and attack. Meanwhile, the center-half adjusted by positioning themselves slightly deeper and adopting a more anchored stance on the field.
In the United Kingdom, there was a noticeable evolution in the roles of full-backs and half-backs. As inside-forwards began to drop back more frequently, the centre-half also retreated significantly, effectively transforming into a third defender. With this shift, wing-halves moved inward to fill the gap left by the centre-half while full-backs extended their positions outward. The traditional W formation of defense gradually morphed into an M shape. At this point, full-backs remained predominantly defensive players; however, as teams transitioned from three defenders to four and wingers started to play closer together, it created opportunities for wide defenders to once again take on the role of half-backs.
How Media Shaped Football Tactics: The Legacy of W-M and the Evolution of Language
The text emphasizes the significant role that media and language play in shaping public perceptions of football tactics. Historically, the W-M formation reigned supreme for many years, yet the persistent reliance on outdated terminology and traditional line-up displays by media outlets has created a gap between what occurs on the field and how it is understood by fans. This situation underscores the notion that early media developments can influence public comprehension and potentially hinder the acceptance of innovative tactical strategies. A closer examination of how media facilitated the shift from W-M to contemporary formations could provide valuable insights into the relationship between language, audience perception, and tactical evolution.Furthermore, this transition was not merely a sudden change but rather a gradual progression towards what can be described as a "hybrid" understanding of player positions. The legacy of hybrid terminology—rooted in the enduring influence of W-M—remains relevant today, illustrating how entrenched language and cultural practices are within sports history. Investigating specific terms used during this transitional phase in comparison with current vernacular would offer a richer understanding of football's linguistic evolution and highlight how historical influences continue to shape modern terminologies.
The 3-4-3 formation has gained traction in modern football due to its flexibility and attacking prowess. This tactical setup allows teams to maintain a strong presence in the midfield while also providing numerous options for forward play. By utilizing three central defenders, teams can secure their defensive line, allowing wing-backs to push up and support the attack effectively. This configuration not only enhances offensive capabilities but also offers a robust framework for defense when needed.}
{One of the key advantages of the 3-4-3 is its ability to dominate possession. With four players in midfield, teams can easily control the game's tempo, making it difficult for opponents to regain possession or create opportunities. The triangular formations that often result from this setup facilitate quick passing sequences and allow players to exploit gaps in the opposition's defense. As a result, teams employing this formation frequently find success in creating goal-scoring chances through fluid movement and coordinated plays.}
{Moreover, the versatility inherent in the 3-4-3 allows coaches to adapt their strategies mid-game based on how their opponents are performing. If an opposing team is pressuring heavily, coaches can instruct their wing-backs to drop back into more defensive roles or even shift into a five-man backline temporarily. Conversely, if they need more goals late in matches, they can encourage their defenders and midfielders to push forward further into attacking positions without compromising overall stability. This adaptability makes the 3-4-3 an appealing choice for managers looking for dynamic tactics during matches.}
{However, despite its strengths, implementing a successful 3-4-3 requires players with specific skill sets and tactical awareness. Wing-backs must possess exceptional stamina and pace since they need to cover large areas of the pitch both offensively and defensively consistently. Central defenders should be adept at reading the game and capable of forming solid partnerships with each other while being ready for quick transitions when counter-attacks occur by opposing teams—this highlights how crucial teamwork is within this system for optimal effectiveness on match day.
From Centralized Control to Decentralized Coverage: The Evolution of M-Defense in Football
"**1. M-Defense Evolution: A Shift from Centralized Control to Decentralized Coverage:** The evolution of the M-defense strategy marks a significant transition in football tactics. Previously, this strategy emphasized central control with midfielders positioned closely together. In contrast, contemporary interpretations have shifted toward decentralized coverage, focusing on wider areas of the pitch and leveraging wing players who operate more autonomously from the main defensive unit. This change highlights an emphasis on territorial dominance rather than solely individual pressure, likely driven by the growing importance of wide play and evolving tactical responses to counteract it.","**2. The 'Retuning Winger' as a Hybrid Role: A Tactical Puzzle for Opponents:** The introduction of the 'retuning winger' role adds complexity to modern football tactics. This hybrid position combines the attacking flair typical of traditional wingers with defensive responsibilities that support full-backs. Consequently, this role complicates conventional tactical frameworks by merging offensive and defensive functions. For opponents, effectively containing both the attacking capabilities and defensive duties associated with retuning wingers requires adaptations in their own defensive formations. The rise of such multifaceted roles underscores the increasing intricacy of football today and highlights an ongoing demand for tactical innovation."
Deep Space 9

The False 9: A Tactical Masterclass in Adaptability
**1. The False 9 as a Tactical Adaptability Tool:** In modern football, the 'False 9' serves not merely as a position but as an essential tactical instrument that adapts to various opponents and game situations. Coaches deploy this role strategically to:* **Disrupt compact defenses:** By dropping deeper into midfield, the False 9 draws defenders away from their positions, thereby opening space for wingers and midfielders to penetrate.
* **Enhance counter-attacking potential:** The False 9 can seamlessly transition into a traditional striker role, facilitating rapid counter-attacks that catch opponents off guard.
* **Create numerical superiority in midfield:** This player contributes to controlling possession and orchestrating build-up play by effectively overloads in the central areas.
Such adaptability underscores the value of the False 9 in contemporary football, where tactical complexity and fluidity are paramount.}
{**2. The Evolution of the False 9 and its Impact on Player Development:** The evolution of the False 9 has been notable, leading to distinct profiles that highlight its significance in player development.
* **Traditional False 9:** Legends like Di Stefano and Cruyff defined this role by balancing playmaking with goal-scoring abilities.
* **Modern 'Midfielder-Forward' False 9:** Contemporary players such as Messi and Kane embody a blend of technical finesse typically associated with midfielders while retaining finishing prowess akin to strikers. They excel at creating intricate passing networks and orchestrating offensive plays, effectively blurring positional boundaries.
This transformation necessitates a new caliber of athlete who can adapt within dynamic systems—highlighting the need for training programs focused on enhancing technical skills, tactical intelligence, and versatility among aspiring footballers.
A centre-forward can take on an even more versatile role by positioning himself behind his teammates in a reverse forward formation. In this setup, he allows his fellow forwards to lead the attack while focusing on facilitating their connection with the rest of the squad. This approach not only enhances team dynamics but also enables him to find opportunities to score goals himself.
The traditional deep centre-forward has always been a rare breed in football, yet they still exist today. Much like the attacking centre-half, this position hasn't completely vanished; however, it rarely receives the recognition it deserves in contemporary discussions. One of the most notable examples of an English team successfully employing a M-M formation in recent years was Leicester City's triumph in the 2021 FA Cup Final. Although Ayoze Perez was often labeled as a "Number 10" and found himself drifting into an inside-left role alongside Vardy, he initially began the match positioned between Vardy and Kelechi Iheanacho.

The precise origin of the deep centre-forward role remains somewhat unclear; however, historical records indicate that this tactic was employed in Argentina over a century ago. Notably, Independiente utilized Luis Ravaschino positioned at the base of a V-shaped forward line. Similarly, Manchester United's lineup from 2007 to 2009 occasionally adopted a comparable structure, featuring two dynamic wingers and two strikers who preferred to retreat into midfield, with Paul Scholes orchestrating play from behind them.

Tactical Flexibility and Adaptability: The Cornerstones of Modern Football
In modern football, tactical flexibility and adaptability have become paramount. Teams often employ formations that can shift fluidly during a match to respond effectively to their opponents' strategies. For instance, utilizing overlapping wing-backs allows a team to transition into a more aggressive 2-4-4 formation, enhancing their attacking width and making it easier to exploit defensive weaknesses. This dynamic approach not only keeps opponents guessing but also facilitates strategic mismatches throughout the game.Additionally, the evolution of player roles such as the 'false 9' has added layers of complexity to team dynamics. The contemporary interpretation of this position involves players who blend traditional centre-forward responsibilities with those of deep-lying playmakers. By acting as focal points for build-up play while still contributing significantly to goal-scoring opportunities, these players exemplify a more multifaceted understanding of positioning on the pitch. This development underscores the increasing importance of tactical intelligence and adaptability in achieving success in today’s football landscape.
Beyond the Pyramid: Modern Formations Demand a More Flexible Approach
1. The limitations of the "pyramid" framework in describing modern formations: The traditional "pyramid" model often falls short in accurately representing the complexities of contemporary football formations, which frequently diverge from this established structure. This limitation raises a pertinent question for analysts and coaches alike: how can one effectively analyze and communicate the intricate nature of these modern systems? There is a pressing need to adopt a more nuanced and adaptable approach that transcends the rigid boundaries of the "pyramid" paradigm, allowing for a deeper understanding of current tactical configurations.}{2. The need for clarity and consistency in sports discourse: Clear communication is paramount in football analysis, yet the field grapples with significant challenges stemming from inconsistent terminology. This lack of uniformity can lead to confusion and misinterpretations among various audiences, complicating public comprehension of tactical discussions. Additionally, players and coaches often hesitate to share their tactical insights, further obscuring understanding. To address this issue, there is an urgent call for analysts to clarify their language consistently, thereby enhancing the intelligibility of their analyses. Such efforts will ultimately enrich discourse within the sport and foster a deeper appreciation among both fans and experts alike.
References
Formations: football tactics explained
We dive into the strengths and weaknesses of the main football tactics and formations: 4-3-3, 4-2-3-1, 4-4-2, 4-4-2 diamond, 3-5 ...
Source: The Coaches' Voicetactical-board.com: Tactical Board Online - Football (Soccer)
Online tactical board for more than 35 different sports (football, futsal, american football, beach football, australian football, rugby, basketball, ...
Source: tactical-board.comTotal Football Analysis Magazine - Tactics, Scouting, Stats
Discover in-depth football analysis, tactics, and scouting reports at Total Football Analysis. Stay ahead with expert insights & data-driven articles.
Source: Total Football AnalysisFootball tactics and formations - ShareMyTactics.com
Create and share your football formations and tactics.
Source: ShareMyTactics.comThe Best 10 Football Tactics Ever ( With Pictures)
Tactics such as VERROU and WM, which are among the best football techniques, have been replaced by different new tactics over time.
Source: Ekip GrassAssociation football tactics and skills
Attacking · Pass and move: Having the ball in their possession, the player needs to choose quickly whether to pass it or not. · ...
Source: WikipediaFootball - Tactics, Positions, Formations
Tactics reflect the importance of planning for matches. Tactics create a playing system that links a team's formation to a ...
Source: BritannicaFootball Tactics - Best football tactics, tips and strategies
Best football tactics, tips and strategies.
Source: football-tactics.com


 ALL
ALL sports
sports
Discussions